What Is the Internet? Meaning, Working, and Types
 |
| What Is The Internet |
The internet has transformed the way we live, work, and communicate, becoming an essential part of our daily lives. But have you ever wondered what exactly the internet is? In this blog post, we will demystify the internet, exploring its origins, infrastructure, and its profound impact on the modern world. From its humble beginnings to its current state as a global network connecting billions of people and devices, we will delve into the fundamental workings and significance of this revolutionary technological marvel.
Definition Of Internet
The internet is a vast interconnected network of computers and devices worldwide. It enables the sharing of information, communication, and access to a multitude of online services.
History of Internet
The internet traces its origins to the ARPANET project in the 1960s, a network created by the U.S. Department of Defense. Over the decades, it expanded, evolved, and became more accessible, leading to its widespread adoption.
Internet vs World Wide Web
It's important to differentiate between the internet and the World Wide Web (WWW). While the internet refers to the underlying network infrastructure, the WWW is an application layer that allows users to access webpages and resources through web browsers.
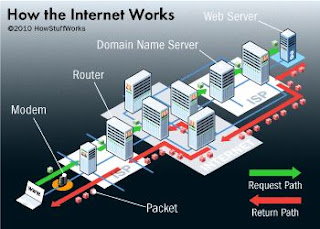
How Does the Internet Work?
1) Infrastructure
The internet's infrastructure consists of physical components such as fiber optic cables, routers, switches, data centers, and satellites. These elements enable the transmission and routing of data packets across vast distances.
2) Protocols and Standards
The internet operates on a set of protocols and standards that govern data transmission and communication. Key protocols include the Internet Protocol (IP), Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), Domain Name System (DNS), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
3) Packet Switching
Data transmitted over the internet is divided into small packets, each containing a portion of the information along with addressing details. These packets are independently routed and reassembled at their destination.
3 Types of Internet Connections
1) Broadband
Broadband connections, such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable, and fiber optics, offer high-speed internet access, enabling fast data transfer and multimedia streaming.
2) Dial-up
Dial-up connections use telephone lines to establish a connection. While significantly slower than broadband, dial-up remains available in some areas where high-speed options are limited.
3) Wireless
Wireless connections, including Wi-Fi, cellular networks (3G, 4G, 5G), and satellite connections, provide internet access without physical wired connections, allowing flexibility and mobility.
Applications and Impact of the Internet
1) Communication and Collaboration
2) Information and Knowledge Sharing
The internet serves as an extensive repository of information, with search engines, online encyclopedias, digital libraries, and educational resources empowering users to access knowledge on various subjects.
3) E-commerce and Online Services
4) Social and Cultural Impact
The internet has reshaped social dynamics, fostering online communities, content creation, and global cultural exchange. It has also raised concerns about privacy, cyber threats, and the digital divide.
4 Type of Internet Services and Impact
1) World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW) is a vast collection of interconnected documents and resources accessible through web browsers. It revolutionized information sharing, enabling easy access to websites, online content, and e-commerce.
2) Email and Communication
Email transformed communication, allowing instant correspondence across the globe. Chat applications, voice and video calling services, and social media platforms further enhanced online interaction and connectivity.
3) E-Commerce and Online Services
The internet opened up new opportunities for businesses and consumers. E-commerce platforms enable online shopping, while online services encompass everything from banking and education to entertainment and healthcare.
4) Information and Knowledge Sharing
The internet provides a vast repository of information, fostering knowledge sharing and learning. Search engines, online libraries, and educational resources empower individuals to access information on virtually any topic.
conclusion
The internet has become an indispensable part of our lives, driving global connectivity, communication, and access to information and services. Understanding the meaning, working, and types of the internet allows us to appreciate its vast reach and impact. As the internet continues to evolve and shape our world, it is crucial to leverage its potential responsibly, address its challenges, and ensure inclusivity, privacy, and security to create a digital environment that benefits individuals, societies, and economies alike.










0 Comments